
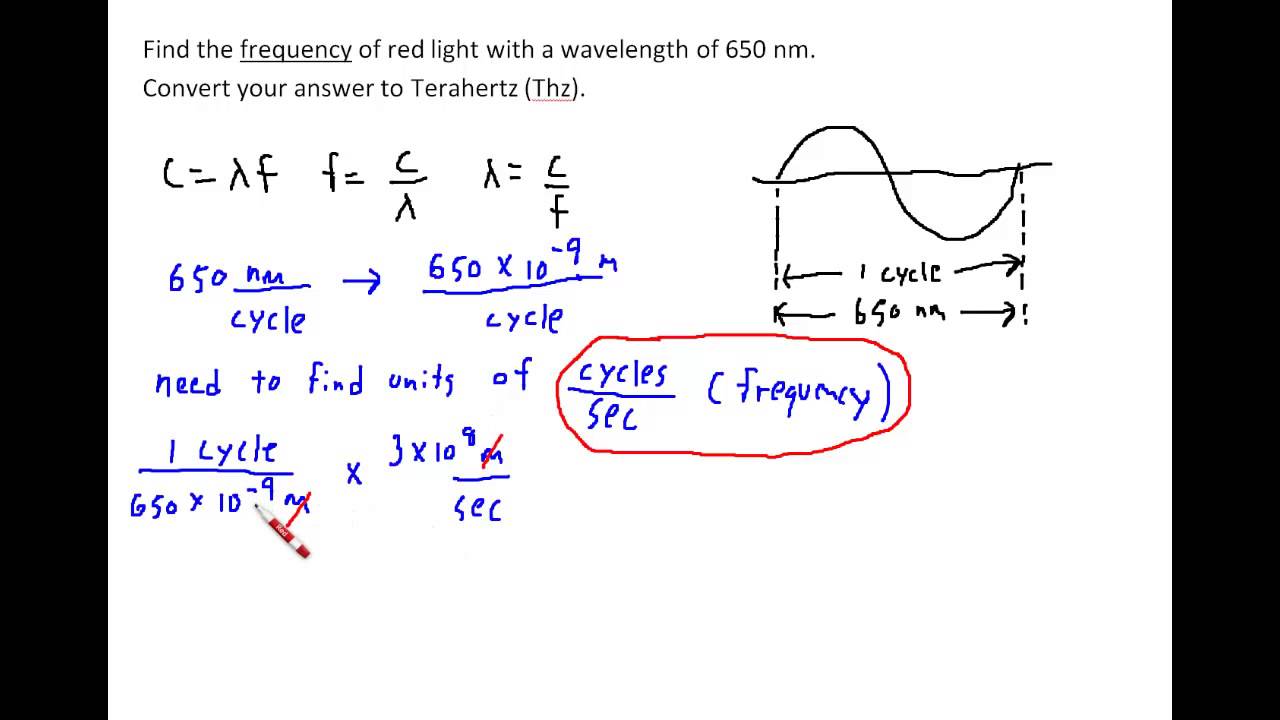
The results have allowed us to assess the effect of temperature and hydrocarbon chain composition on bilayer structure. Bilayer parameters, such as area per lipid and overall bilayer thickness have been obtained in conjunction with intrabilayer structural parameters (e.g. The structural parameters of fluid phase bilayers composed of phosphatidylcholines with fully saturated, mixed, and branched fatty acid chains, at several temperatures, have been determined by simultaneously analyzing small-angle neutron and X-ray scattering data.

While the GBBR designs are intended for metamorphic solar cells, the broad and high reflection may also be useful for other optoelectronic devices such as light-emitting diodes or lasers. Small deviations between the calculated AlGaInAs and utilized AlGaAs refractive index exist, giving methods for future GBBR improvement. Minimal crosshatch roughness and unintentional thickness variation occur throughout the buffer, which likely influences reflection slightly. We also analyze potential deviations in a baseline GBBR from that of a perfect DBR using transmission electron microscopy to analyze imperfections in the material and modeling to analyze the impact of imperfect refractive index data for lattice-mismatched AlGaInAs. A GBBR with a reflection of 99% is demonstrated, as well as a triple GBBR that has over 80% reflection for 100?nm of the spectrum around 800?nm. Apodized and triple GBBRs are demonstrated, and transparency is always considered, requiring designs with carefully engineered material combinations.

We design buffers that provide (1) high reflectivity over a narrow bandwidth, for quantum well solar cells, (2) reflectivity over a wide bandwidth, for optically thin solar cells, and (3) low sidelobe reflection, for multijunction devices that demand low out-of-band more » reflection. Here, we design and demonstrate complex GBBRs for specific metamorphic solar cell applications. Prior work showed that these properties can be combined with low threading dislocation density and high reflectivity. « lessĪ graded buffer Bragg reflector (GBBR) is a bifunctional device component that provides the reflection of a distributed Bragg reflector and the adjustable lattice constant of a compositionally graded buffer. Instead, a more complicated light distribution was measured for these three materials. The measured light reflectance distribution was measured to be specular for several ESR films as well as for aluminum foil, mostly diffuse for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) tape and titanium dioxide paint, and neither specular nor diffuse for Lumirror(R), Melinex(R) and Tyvek(R). The dynamic range for the current measurements is 105:1. Each photodiode subtends 6.3o, and the photodiode array can be positioned at any angle with up to 10 arc minute angular resolution. The laser can be positioned at any angle with a position accuracy of 10 arc minutes. A LabVIEW program controls the motion of the laser and the photodiode array, the multiplexer, and the data collection. The light-induced current is, through a multiplexer, read more » out with a digital multimeter. The photodiodes are movable to cover 2 pi of solid angle. The reflected light's angular distribution is measured by an array of silicon photodiodes. A 440 nm, output power stabilized, un-polarized laser is shone onto a reflector at a fixed angle of incidence. In this paper we measure the optical reflectance distribution for eleven commonly used reflectors. Since light reflectance is poorly understood, either purely specular or purely diffuse reflectance is generally assumed. When simulating light collection in scintillators, modeling the angular distribution of optical light reflectance from surfaces is very important.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
